Globally, pesticide pollution in surface water is becoming increasingly serious. Due to the widespread use of pesticides in agriculture, the increase of environmental pollutants such as pesticides in surface water has become the top priority of public drinking water quality control. These pollutants not only threaten the ecological balance but also seriously affect public health, potentially causing damage to the eye, liver, kidney and spleen and increasing the risk of anemia and cancer.

Pesticide reatment technology in water samples
There are many sample preparation techniques for extracting, enriching and purifying pesticides from water samples, including common Liquid-liquid Extraction (LLE), Solid Phase Extraction (SPE), and Thin Film Microextraction (TFME) Solid Phase Microextraction (SPME). Thin Film Microextraction (TFME) and Solid Phase Microextraction (SPME) stand out for their environment-friendly characteristics, not only without a large number of organic solvents, reduce the use of chemicals and waste production, but also have efficient sample enrichment and purification capacity, providing a more environmentally friendly, efficient and low-cost alternative.
This paper mainly introduces Thin Film Microextraction (TFME) technology as an alternative to Liquid-liquid Extraction (LLE), as an extension of the SPME method, to further improve the technical sensitivity by increasing the coating volume to reach a lower detection limit.
Overview of Thin Film Microextraction (TFME) technology
Thin Film Solid Phase Microextraction, or TFME, or Thin Film SPME or TF-SPME, developed from SPME, is a balanced extraction technique.
Technological Superiority
● High efficiency and accuracy: TFME improves the volume of the extracted phase, increases the adsorption capacity and greatly improves the sensitivity, so that the extremely trace pesticide residues in surface water can also be accurately detected;
● Environmental protection: TFME technology significantly reduces the use of organic solvents, reduce the burden on the environment, is a green analysis method;
● Wide applicability: wide polar range, especially suitable for customers without target analysis, suitable for pesticide residue analysis in a variety of water quality environments.
Scientific research verification and practical application
TF-SPME Thin Film Solid-phase Microextraction for the analysis of cultivated pesticide residues in surface water applications [1]
TF-SPME method
● Sample source: Waterloo Grand River, Ontario, Canada
● Sample processing: LLE, in-bottle TFME, and field TFME
● TF-SPME: coated PDMS / DVB, bottle sampling: room temperature, 1L sample, equilibrated; field sampling: extraction time is 10 minutes, stirring rate is 2000 rpm, then resolved in portable GC / MS.

Figure 1: Extraction in the TF-SPME sample flask

Figure 2: Field sampling using TFME with drill bit, portable G C/MS
>>> Results and discussion
Table 1:TF-SPME analysis result in the bottles
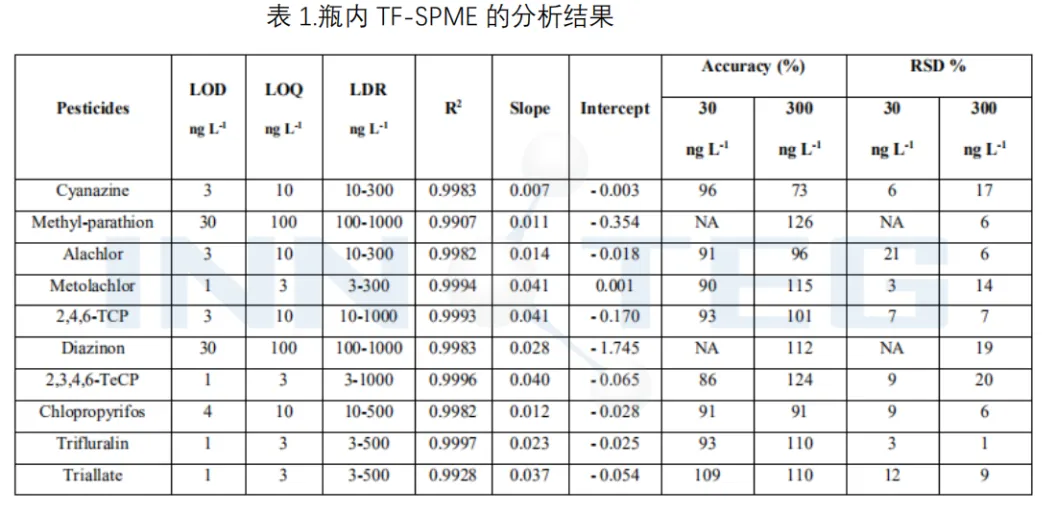
Table 2. Comparison of surface water test results between TF-SPME and LLE methods in the bottles
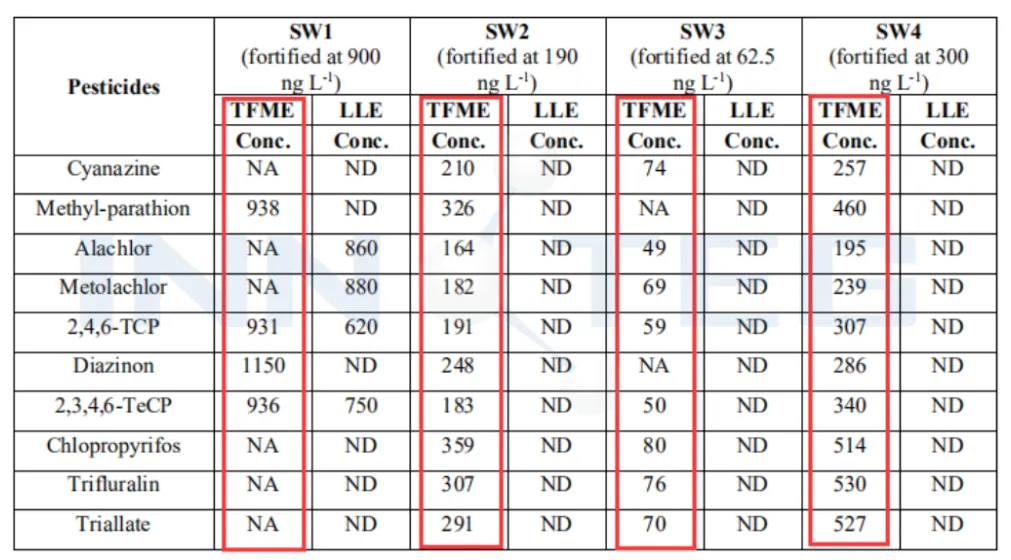
From the above table, the TFME method has obtained low detection limit and quantitative limit, LOD: 1-30 ng / L and LOO.3 – 100 ng /, the linear correlation coefficient R'is 0.990 – 0.999, and the sensitivity is 2 – 3 orders of magnitude higher than that obtained by the detection limit-based US EPA 8270 method.
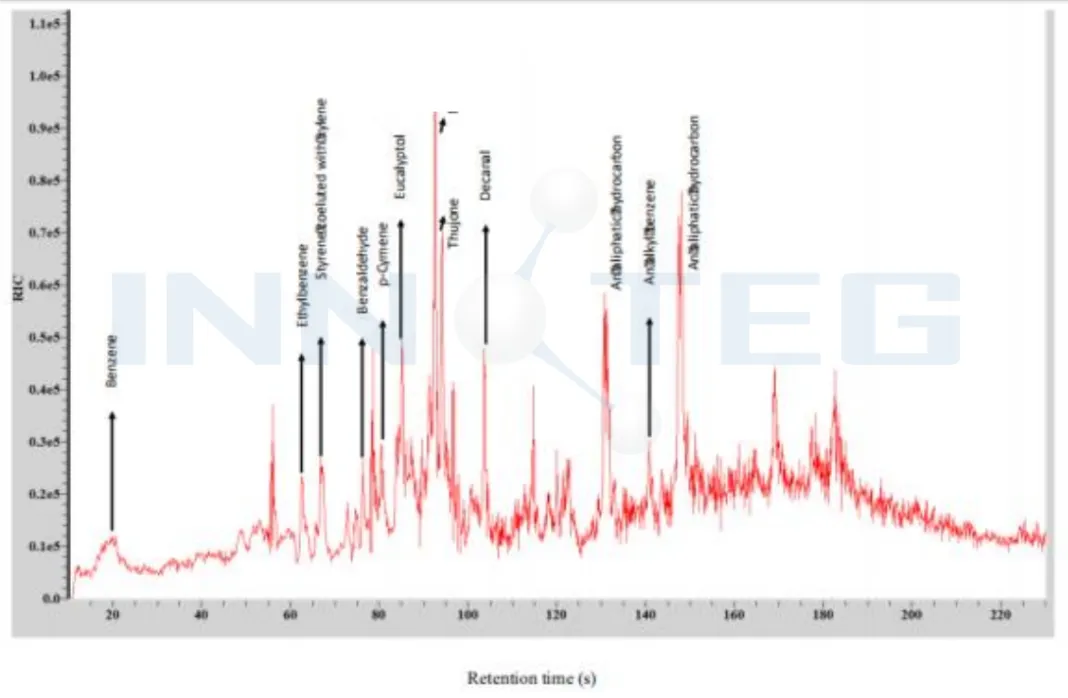
Figure 3: Portable G C/MS spectrum of field TF-SPME sampling
According to the field TF-SPME map, the traditional method of liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) due to the transfer of water samples from the sampling point to the laboratory and degradation during the transportation, making the compounds with moderate to high hydrophobicity, TF-SPME can be used for field sampling, eliminating the process of transporting samples to the laboratory, and no organic solvent, green, is one of the best choice for environmental monitoring.
The above cases fully illustrate the advantages of TF: the perfection of efficiency and sensitivity.
INNOTEG TF-SPME product information
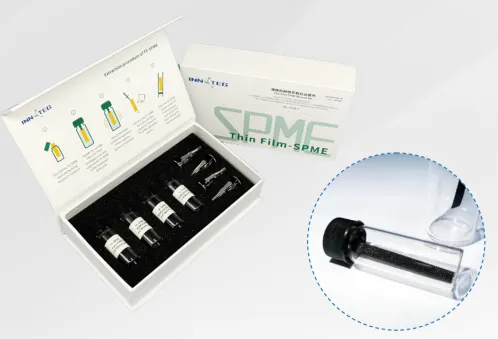
Various coatings and specifications of the membrane
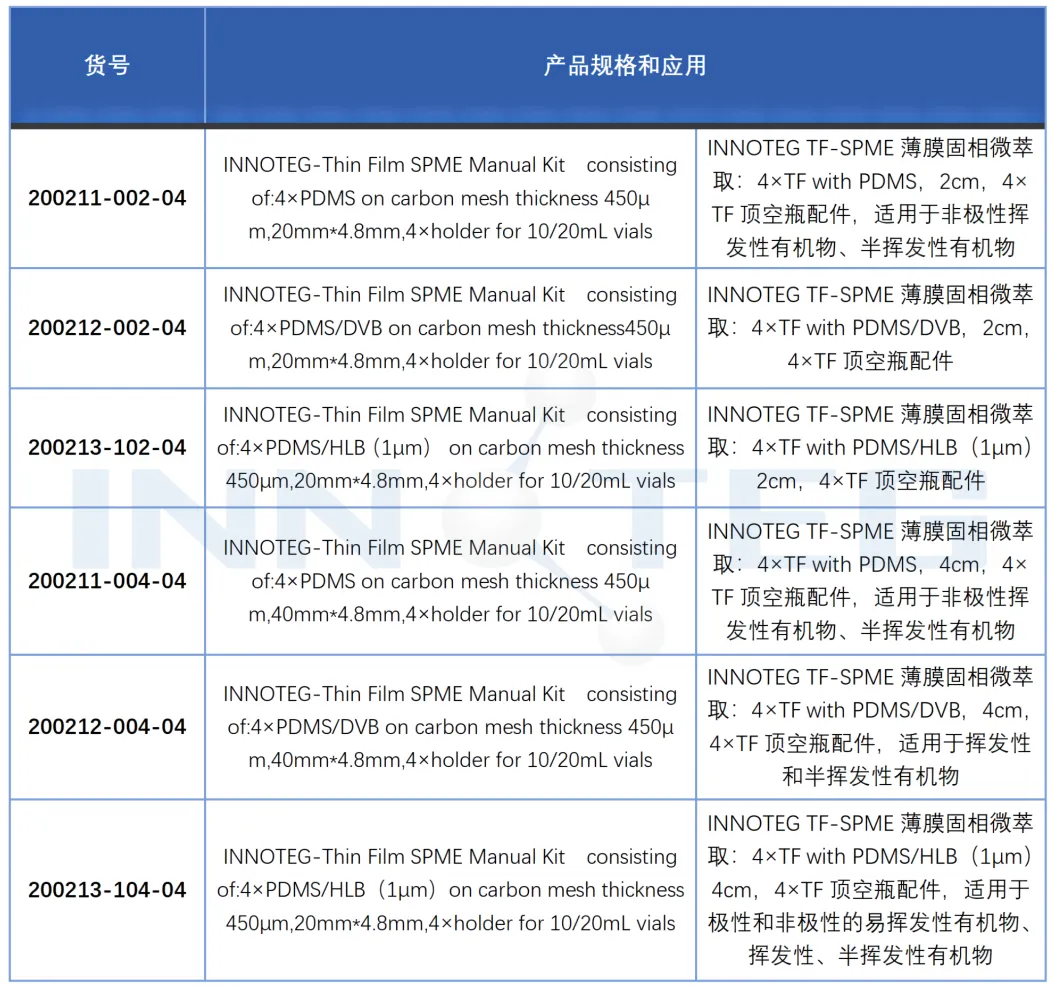
Two specifications: 20mmx4.8mm,40mmx4.8mm
Three adsorbents:
PDMS: suitable for the analysis of the nonpolar compounds VOCs and SVOCS
PDMS / DVB: suitable for the analysis of nonpolar and moderately polar volatile organic compounds and solid wastes, with higher adsorption efficiency
PDMS / HLB: Excellent adsorption capacity for compounds with a wide polar range is suitable for nonpolar, moderately polar and polar VOCs, SVOCs analysis
For purchase,please Email:[email protected]

2 Comment(s)
1
1
1
1
1
Leave a Comment